Adverse Reactions
Frequently Observed
The most frequently reported adverse reactions are drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and intoxicated feeling.
Infrequently Observed
All adverse events tabulated below are classified as infrequent.
Central Nervous System: headache, shaky feeling, tingling, agitation, fainting, fatigue, heavy eyelids, high energy, hot spells, numbness, sluggishness, seizure. Mental confusion, excitement or depression can also occur due to intolerance, particularly in elderly or debilitated patients, or due to overdosage of butalbital.
Autonomic Nervous System: dry mouth, hyperhidrosis.
Gastrointestinal: difficulty swallowing, heartburn, flatulence, constipation.
Cardiovascular: tachycardia.
Musculoskeletal: leg pain, muscle fatigue.
Genitourinary: diuresis.
Miscellaneous: pruritus, fever, earache, nasal congestion, tinnitus, euphoria, allergic reactions.
Several cases of dermatological reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme, have been reported.
The following adverse drug events may be borne in mind as potential effects of the components of this product. Potential effects of high dosage are listed in the OVERDOSAGE section.
Acetaminophen: allergic reactions, rash, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis.
Caffeine: cardiac stimulation, irritability, tremor, dependence, nephrotoxicity, hyperglycemia.
Frequently Observed
The most frequently reported adverse reactions are drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and intoxicated feeling.
Infrequently Observed
All adverse events tabulated below are classified as infrequent.
Central Nervous System: headache, shaky feeling, tingling, agitation, fainting, fatigue, heavy eyelids, high energy, hot spells, numbness, sluggishness, seizure. Mental confusion, excitement or depression can also occur due to intolerance, particularly in elderly or debilitated patients, or due to overdosage of butalbital.
Autonomic Nervous System: dry mouth, hyperhidrosis.
Gastrointestinal: difficulty swallowing, heartburn, flatulence, constipation.
Cardiovascular: tachycardia.
Musculoskeletal: leg pain, muscle fatigue.
Genitourinary: diuresis.
Miscellaneous: pruritus, fever, earache, nasal congestion, tinnitus, euphoria, allergic reactions. Several cases of dermatological reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme, have been reported.
The following adverse drug events may be borne in mind as potential effects of the components of this product. Potential effects of high dos age are listed in the OVERDOSAGE section.
Acetaminophen: allergic reactions, rash, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis.
Caffeine: cardiac stimulation, irritability, tremor, dependence, nephrotoxicity, hyperglycemia.
Drug Abuse And Dependence
Abuse and Dependee
Butalbital
Barbiturates may be habit-forming: Tolerance, psychological dependence, and physical dependence may occur especially following prolonged use of high doses of barbiturates. The average daily dose for the barbiturate addict is usually about 1500 mg. As tolerance to barbiturates develops, the amount needed to maintain the same level of intoxication increases; tolerance to a fatal dosage, however, does not increase more than two-fold. As this occurs, the margin between an intoxication dosage and fatal dosage becomes smaller. The lethal dose of a barbiturate is far less if alcohol is also ingested. Major withdrawal symptoms (convulsions and delirium) may occur within 16 hours and last up to 5 days after abrupt cessation of these drugs. Intensity of withdrawal symptoms gradually declines over a period of approximately 15 days. Treatment of barbiturate dependence consists of cautious and gradual withdrawal of the drug. Barbiturate-dependent patients can be withdrawn by using a number of different withdrawal regimens. One method involves initiating treatment at the patient’s regular dosage level and gradually decreasing the daily dosage as tolerated by the patient.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
The CNS effects of butalbital may be enhanced by monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors.
Butalbital, acetaminophen and caffeine may enhance the effects of: other narcotic analgesics, alcohol, general anesthetics, tranquilizers such as chlordiazepoxide, sedative-hypnotics, or other CNS depressants, causing increased CNS depression.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Acetaminophen may produce false-positive test results for urinary 5-hydroxy-indoleacetic acid.






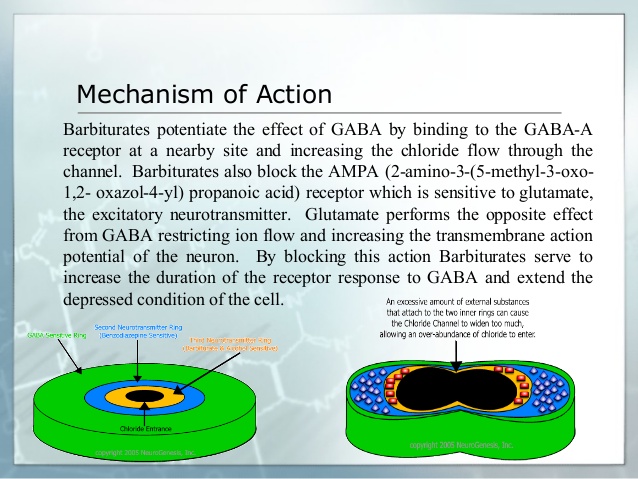
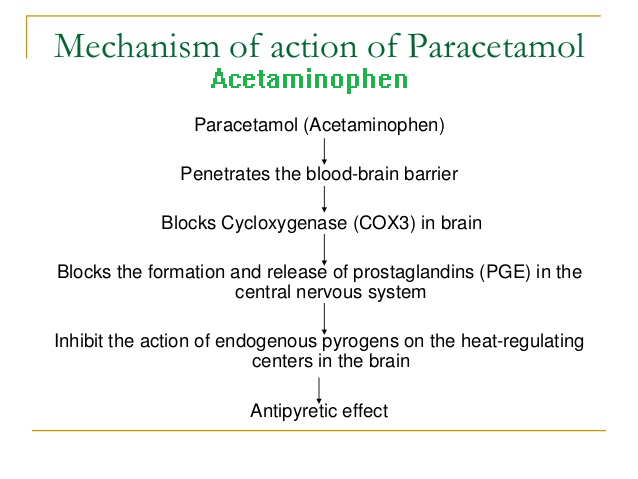 Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen acts primarily in the CNS and increases the pain threshold by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, an enzyme involved in prostaglandin (PG) synthesis. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is generally considered to be a weak inhibitor of the synthesis of prostaglandins (PGs). However, the in vivo effects of paracetamol are similar to those of the selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors. Paracetamol also decreases PG concentrations in vivo, but, unlike the selective COX-2 inhibitors, paracetamol does not suppress the inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis. Acetaminophen inhibits both isoforms of central cyclooxygenase, COX-1 and COX-2.
Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen acts primarily in the CNS and increases the pain threshold by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, an enzyme involved in prostaglandin (PG) synthesis. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is generally considered to be a weak inhibitor of the synthesis of prostaglandins (PGs). However, the in vivo effects of paracetamol are similar to those of the selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors. Paracetamol also decreases PG concentrations in vivo, but, unlike the selective COX-2 inhibitors, paracetamol does not suppress the inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis. Acetaminophen inhibits both isoforms of central cyclooxygenase, COX-1 and COX-2.